1.神秘命名
如果想不出一个好的名字,说明背后很可能隐藏着更深的设计问题
看最新的《阿里开发规范1.7 黄山版》
https://developer.aliyun.com/article/888697
2.重复代码
优化:禁止复制粘贴,巧用Method Exact。
坏味道
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| /**
* 计算水果总价(同一个类的两个函数含有相同的表达式)
*
*/
public class FruitsCost {
public double computeMoneyWithoutPrivileges(String type, int numbers) {
double prices;
switch (type) {
case "apple":
prices = 5.5;
break;
case "banana":
prices = 4.0;
break;
case "strawberry":
prices = 10.5;
break;
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal type : " + type);
}
return prices * numbers;
}
public double computeMoneyWithPrivileges(String type, double numbers, double discount) {
double prices;
switch (type) {
case "apple":
prices = 5.5;
break;
case "banana":
prices = 4.0;
break;
case "strawberry":
prices = 10.5;
break;
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal type : " + type);
}
return prices * numbers * discount;
}
}
|
好味道
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| public class FruitsCost {
public double computeMoneyWithoutPrivileges(String type, int numbers) {
double prices = getPrices(type);
return prices * numbers;
}
private double getPrices(String type) {
double prices;
switch (type) {
case "apple":
prices = 5.5;
break;
case "banana":
prices = 4.0;
break;
case "strawberry":
prices = 10.5;
break;
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal type : " + type);
}
return prices;
}
public double computeMoneyWithPrivileges(String type, double numbers, double discount) {
double prices = getPrices(type);
return prices * numbers * discount;
}
}
|
3.过长函数
优化:每个函数建议不超过80行代码,条件、循环、公共集中的过程提取处理
坏味道
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public void doSth3(){
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(String sjs : list){
//doSth,60行
sjs = sjs + "";
}
}
|
好味道
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| public void doSth3(){
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(String sjs : list){
doloop(sjs);
}
}
private static void doloop(String sjs) {
//doSth,60行
sjs = sjs + "";
}
|
4.过长参数列表
优化:使用对象合并参数
坏味道
1
2
3
4
5
| public class Case2 {
public void createUser(String username,String password , Float height , Float weight,Integer age){
}
}
|
好味道
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| 好味道
public class Case2 {
public void createUser(User user){
}
}
public class User {
private String username
private String password;
//...Getter and Setter
}
|
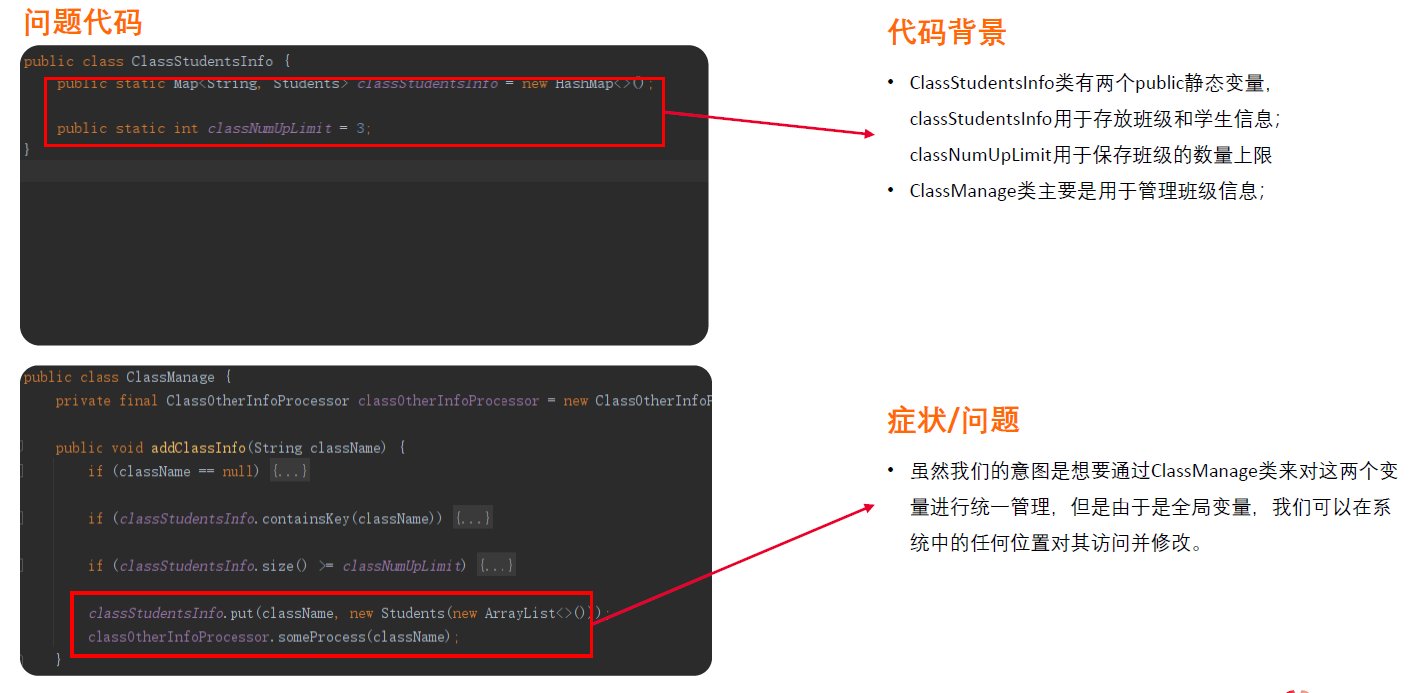
5.全局数据
优化:合并数据到方法、类成员中,最小范围原则
坏味道
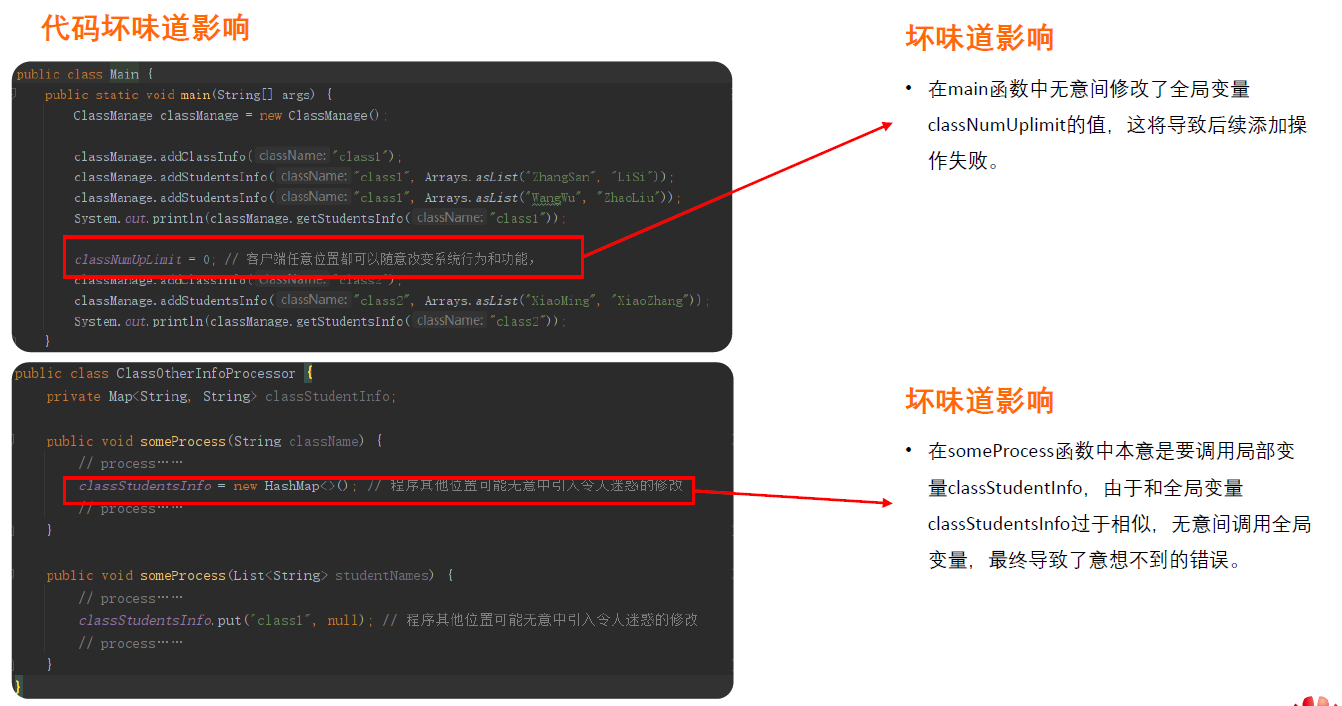
好味道
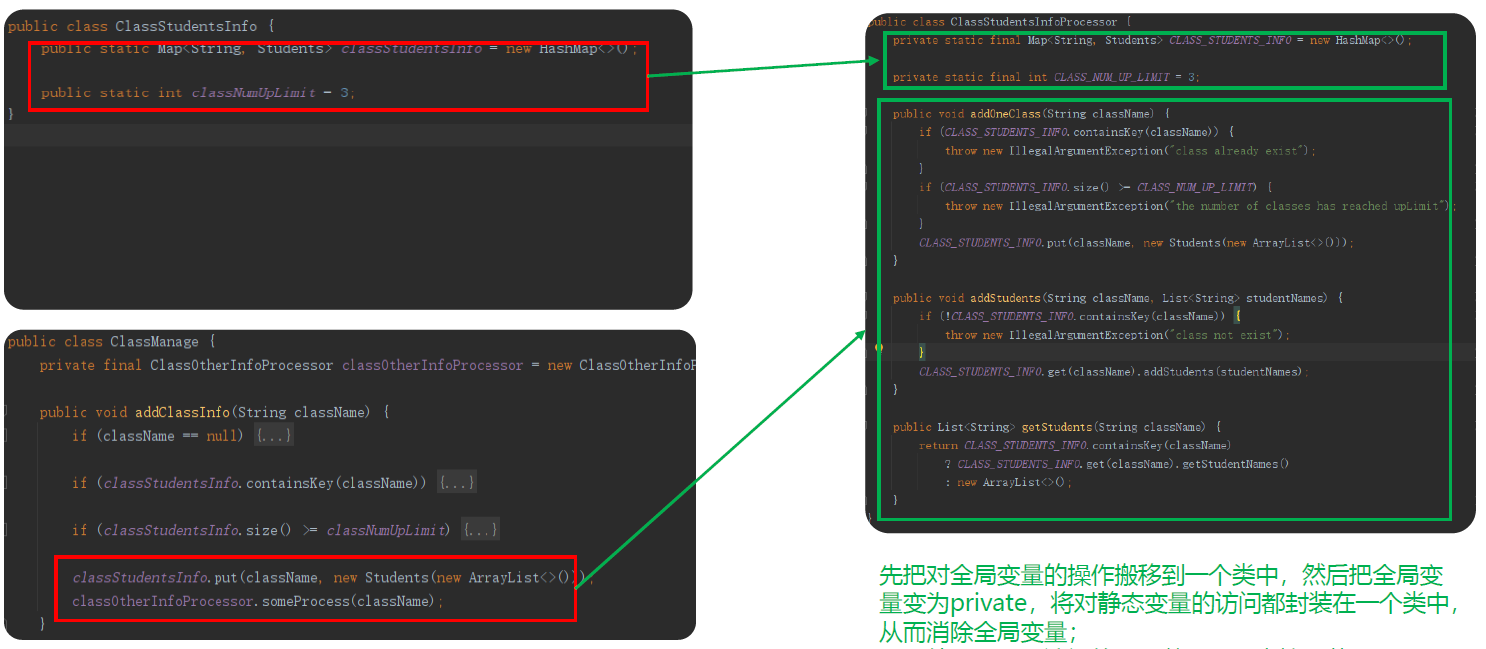
6.可变数据
优化:函数式编程、数据永不改变
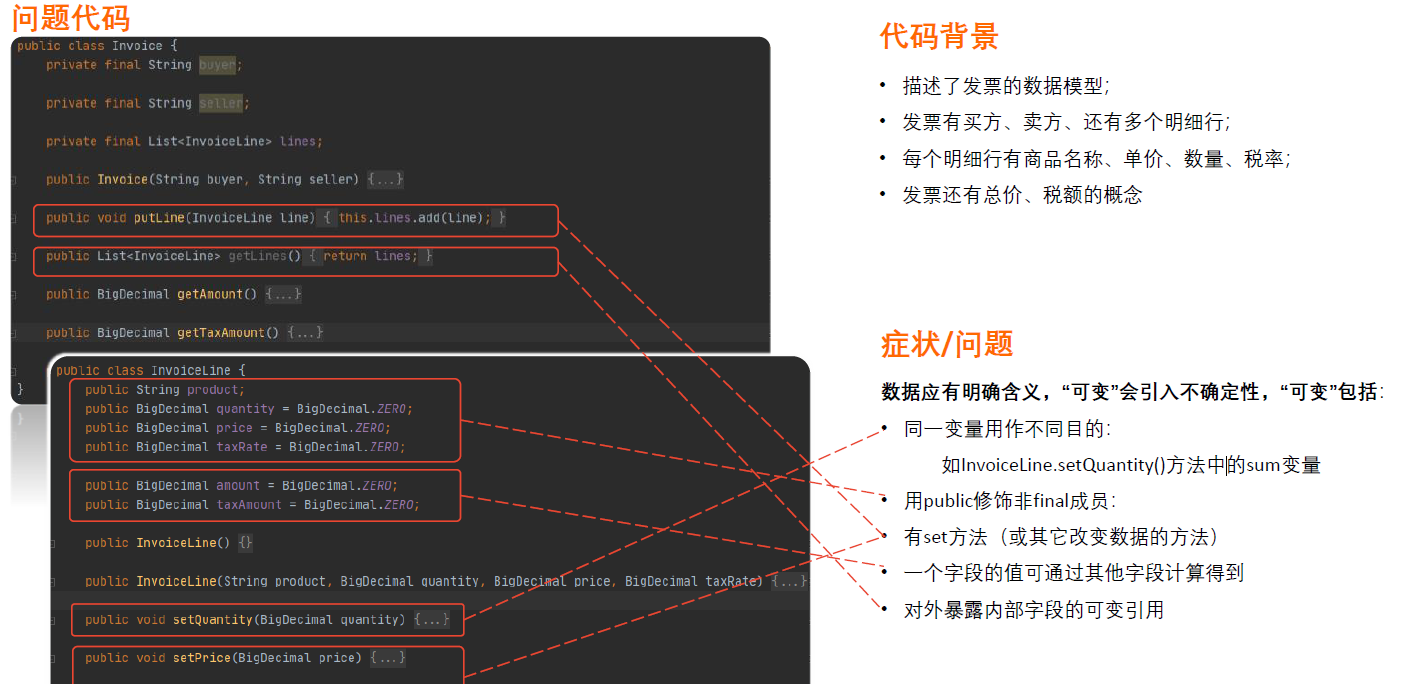
什么是可变数据(Mutable Data)
定义:可变数据——对数据的修改经常导致出乎意料的结果和难以发现的Bug。
影响:影响可维护性,在一处修改数据,却在另一处造成难以发现的破坏
改进目标:应用“数据不可变”:不可变性是强大的代码防腐剂
方法:封装变量、拆分变量、提炼函数、移除设值函数、查询取代派生、Builder模式创建不可变对象、引用对象改为值对象、函数式编程等
注:并非所有可变类型都是不良的,这里关注描述数据的可变类型
坏味道
好味道
可变数据症状
一个变量用作不同目的
数据类型中,用public修饰非final成员
有set方法(或其它改变数据的方法)
一个成员变量的值可通过其他字段计算得到
对外暴露内部变量的可变引用
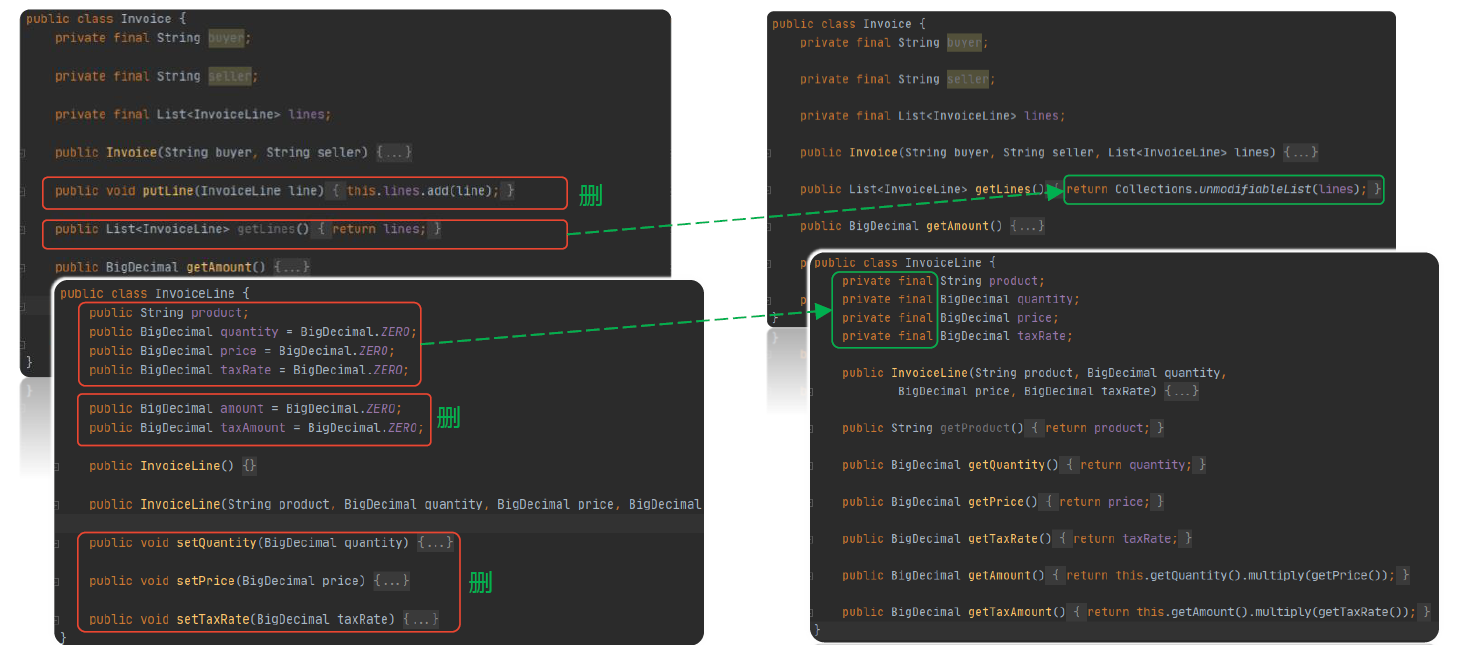
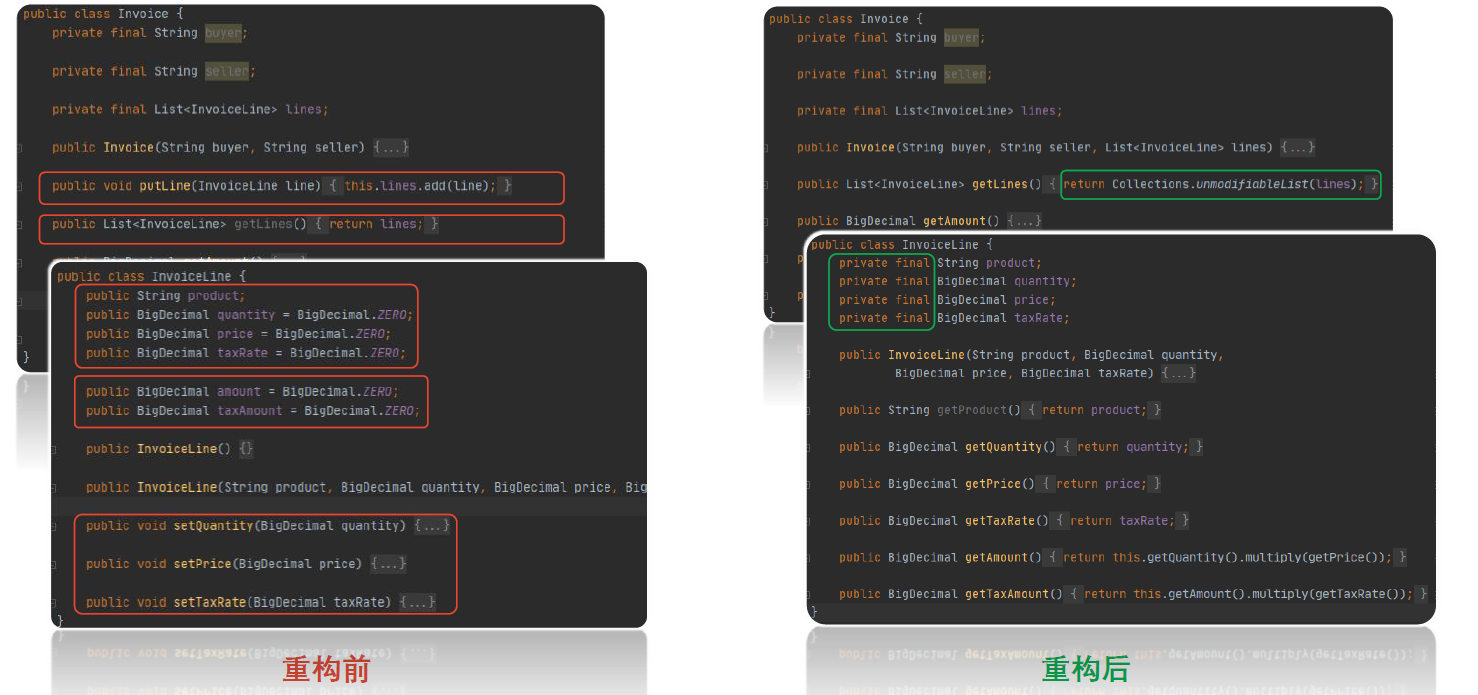
改进手法
封装变量
拆分变量(用提取函数):Ctrl+Atl+M
移除设值函数:用内联移除、直接删除(Ctrl+Alt+N、Alt+Del)
Builder模式创建不可变对象






